The Different Types of Overhead Cranes and Their Uses
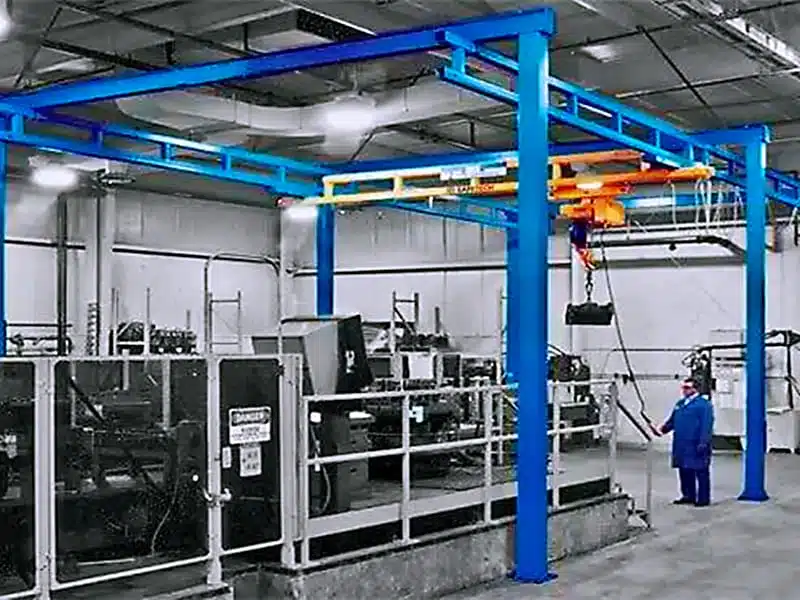

Overhead cranes are vital for handling heavy materials and loads in various industries such as manufacturing, construction, and warehousing. Their versatility allows them to be used in different environments, from small workshops to large industrial plants. The key to their success lies in understanding the different types of overhead crane and choosing the right one for the specific needs of a business or project.
In this article, we will explore the different types of overhead cranes, their features, and the best uses for each. By understanding these variations, businesses can make informed decisions when selecting a crane that improves efficiency, reduces costs, and enhances safety.
What is an Overhead Crane?
An overhead crane, also known as a bridge crane, is a lifting device used to move heavy loads in a horizontal plane. It is typically composed of a bridge (the main horizontal structure), a hoist (the lifting mechanism), and a trolley (which moves the hoist across the bridge). Overhead cranes are often installed on the ceiling or mounted on supporting structures above the ground, which allows them to lift and move materials within a defined space, without taking up valuable floor space.
Overhead cranes come in various types, each designed for specific tasks and environments. The primary differences between these crane types are their configurations, lifting capacities, and usage scenarios. Let’s dive into the most common types of overhead cranes and their specific applications.
1. Single Girder Overhead Crane
Features:
-
A single girder crane consists of one horizontal beam (the girder) supported by two end trucks.
-
The hoist travels along the bridge or girder to move loads.
-
It is a lighter-duty crane, often used for medium-sized lifting tasks.
Best Uses:
Single girder overhead crane are ideal for lighter lifting duties and smaller spaces. These cranes are commonly used in:
-
Warehouses: To move goods or materials across short distances.
-
Small Manufacturing Plants: For lifting components or tools.
-
Assembly Lines: Where small to medium-sized parts need to be moved between workstations.
-
Maintenance Operations: In smaller facilities that require occasional lifting of machinery or equipment.
Single girder cranes are typically more affordable and cost-effective compared to double girder cranes, making them a good option for businesses with lighter load requirements or smaller operations.
2. Double Girder Overhead Crane
Features:
-
A double girder crane uses two parallel beams (girders) to support the hoist, offering greater strength and stability.
-
This design provides a higher lifting capacity and allows for more precise load handling.
-
It is typically used for larger, heavier lifting tasks.
Best Uses:
Double girder overhead cranes are ideal for heavy-duty tasks that require high lifting capacities. These cranes are used in:
-
Heavy Manufacturing: For lifting large and heavy components like steel beams or automotive parts.
-
Steel Mills: Where the crane is used to move molten metal or heavy steel products.
-
Construction Sites: For moving large equipment or structural components.
-
Shipyards: To lift large sections of ships during construction or maintenance.
Double girder cranes are more expensive than single girder cranes but are often the preferred option for industries that require high lifting capacities and robust performance.
3. Underhung Overhead Crane
Features:
-
An underhung crane is mounted to the underside of a building’s roof structure rather than on top of a pair of runways.
-
The hoist and bridge are suspended from the ceiling, providing more clearance in the work area.
-
These cranes are typically lighter and ideal for low-headroom situations.
Best Uses:
Underhung overhead cranes are suitable for applications where space is limited or ceiling height is a concern. They are commonly used in:
-
Small Manufacturing Facilities: Where there’s limited headroom or lower ceilings.
-
Workshops: For handling tools or equipment with precision in tight spaces.
-
Maintenance: For lifting machinery or components in facilities with limited vertical clearance.
-
Tight Areas: For use in industries such as food processing, light assembly, and packaging.
Because of their low profile, underhung cranes are particularly advantageous in spaces where maximizing vertical height is important.
4. Top Running Overhead Crane
Features:
-
Top running cranes are mounted on tracks that run along the top of the building’s structure, which allows them to carry heavier loads.
-
These cranes typically have a larger lifting capacity than underhung cranes and are built for more demanding applications.
Best Uses:
Top running cranes are versatile and used in larger facilities where greater lifting capacities and spans are required. They are common in:
-
Large Manufacturing Plants: For handling heavy and bulky materials.
-
Steel Mills and Foundries: For moving heavy loads like ingots, molds, and molten metal.
-
Construction Sites: For lifting large structural components.
-
Shipyards: To move parts of ships and heavy maritime equipment.
Top running cranes are designed for industrial environments where high efficiency, durability, and strength are crucial.
5. Explosion-Proof Overhead Crane
Features:
-
Explosion-proof cranes are designed to operate in hazardous environments where flammable gases, dust, or other explosive materials are present.
-
These cranes are equipped with special features such as sealed electrical components, specialized motors, and anti-sparking mechanisms to prevent ignition in dangerous environments.
Best Uses:
Explosion-proof overhead cranes are essential for industries dealing with volatile substances. These include:
-
Chemical Plants: For handling chemicals that could be hazardous if exposed to sparks or electrical malfunctions.
-
Oil and Gas: For lifting equipment or materials in refineries or drilling sites where flammable gases are common.
-
Mining: In areas where explosive dust or gases may be present.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Where fine powders or volatile compounds are handled.
Explosion-proof cranes ensure that industries operating in hazardous conditions comply with safety regulations while maintaining a high level of operational efficiency.
6. Jib Cranes (Overhead Hoist) with Extended Reach
Features:
-
Jib cranes are typically smaller, with a mounted arm (jib) that extends outward and rotates.
-
They are often used in combination with larger overhead crane systems to increase reach and flexibility.
Best Uses:
Jib cranes are used in applications where additional reach or flexibility is needed, including:
-
Assembly Lines: To position and maneuver parts in tight spaces.
-
Small Workshops: For moving lightweight loads within a defined area.
-
Shipping Areas: For unloading or loading materials on trucks.
These cranes are an excellent addition to overhead systems, providing added flexibility for smaller operations.
7. Custom Overhead Cranes
Features:
-
Custom cranes are specially designed for specific tasks and industries.
-
These cranes can be built to meet unique lifting requirements, such as non-standard load capacities, spans, or environmental conditions.
Best Uses:
Custom overhead cranes are used in highly specialized industries or applications where off-the-shelf cranes do not meet the specific requirements. They are commonly seen in:
-
Aerospace: For lifting delicate, custom parts or components.
-
Nuclear Power Plants: For handling radioactive materials in specialized environments.
-
Mining: For unique or highly specialized lifting needs.
-
Automotive: For moving large vehicle parts or components in an assembly line.
Custom cranes are built to meet precise specifications, ensuring that operations run smoothly in unique or challenging environments.
Conclusion
Overhead cranes are vital in a wide range of industries, and choosing the right type of crane for your specific application can significantly impact productivity, safety, and efficiency. Whether you are working in a small workshop or a large manufacturing plant, there’s an overhead crane solution designed to meet your needs.
By understanding the various types of overhead cranes—single girder, double girder, underhung, top running, explosion-proof, jib, and custom cranes—you can make an informed decision that best suits the requirements of your business. With the right crane system in place, you’ll be able to improve operations, reduce downtime, and ensure the safety of your employees and materials.