Corrective Jaw Surgery: A Comprehensive Guide
Corrective jaw surgery, also known as orthognathic surgery, is a transformative medical procedure designed to correct irregularities in the jawbone. This surgery improves the alignment and function of the jaw, enhancing both aesthetics and the quality of life. Individuals with jaw misalignment, bite problems, or facial asymmetry may find corrective jaw surgery to be life-changing. This article explores the details of corrective jaw surgery, including its benefits, the surgical process, recovery, and who may be a candidate.
What Is Corrective Jaw Surgery?
Corrective jaw surgery is a procedure performed by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon to address abnormalities in the jawbone and teeth. These irregularities can arise from genetic factors, injury, or developmental issues. The surgery aims to:
- Realign the jaws for improved function and appearance.
- Correct bite problems such as overbite, underbite, or open bite.
- Address speech or breathing difficulties caused by jaw misalignment.
- Enhance facial harmony and symmetry.
Reasons for Corrective Jaw Surgery
People opt for corrective jaw surgery for various medical and cosmetic reasons. Here are some of the most common:
Improved Chewing and Biting
Misaligned jaws can make it difficult to chew and bite food properly. Surgery ensures the upper and lower jaws align correctly, facilitating efficient and comfortable eating.
Speech Improvement
Jaw alignment issues can interfere with clear speech. Surgery can help resolve pronunciation difficulties caused by improper jaw positioning.
Alleviating Jaw Pain
Chronic pain in the jaw joint (temporomandibular joint or TMJ) and headaches caused by misalignment can be relieved through surgery.
Correcting Facial Asymmetry
Facial imbalances such as a protruding jaw, receding chin, or uneven face structure can be addressed, significantly improving aesthetics.
Breathing Issues
Conditions like obstructive sleep apnea, where breathing is interrupted during sleep due to airway obstruction, can be treated by modifying the jaw structure.
The Surgical Process
Corrective jaw surgery is a meticulously planned procedure that involves several stages:
Initial Consultation
The process begins with a detailed consultation with an oral and maxillofacial surgeon. This includes:
- Medical and dental evaluations.
- Imaging such as X-rays, CT scans, or 3D models of the jaw.
- Discussions about goals, expectations, and potential outcomes.
Pre-Surgical Orthodontics
Most patients require orthodontic treatment before surgery to align their teeth. This step ensures that once the jaws are repositioned, the teeth fit together properly. Braces may be worn for 12 to 18 months before the operation.
Surgery
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia and can last between 2 to 5 hours, depending on the complexity. Common techniques include:
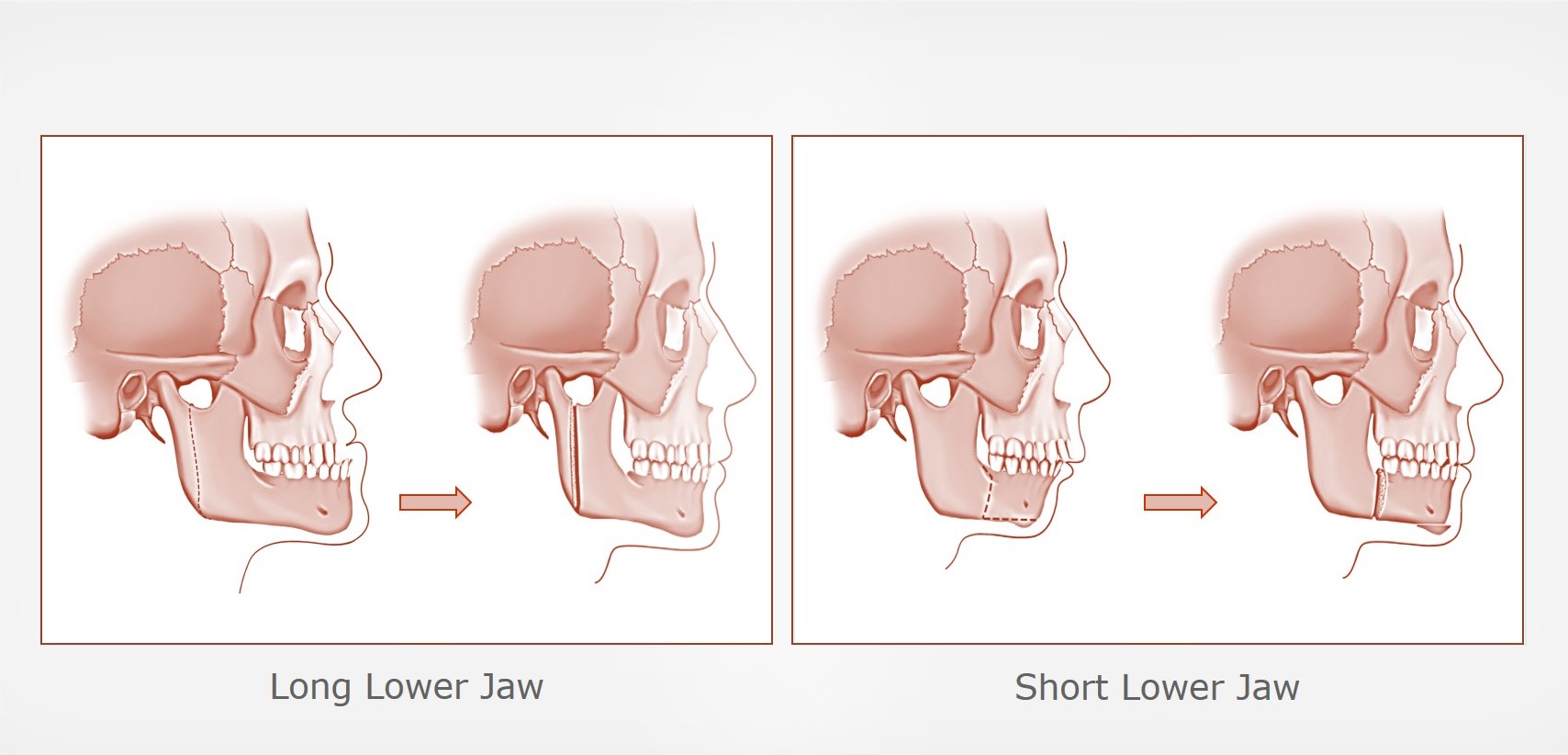
- Upper Jaw Surgery (Maxillary Osteotomy): Adjusts the position of the upper jaw to correct open bite, crossbite, or excessive gum exposure.
- Lower Jaw Surgery (Mandibular Osteotomy): Repositions the lower jaw to address overbite or underbite.
- Chin Surgery (Genioplasty): Reshapes or repositions the chin for better facial harmony.
The surgeon makes incisions inside the mouth to avoid visible scars and uses screws, plates, or wires to secure the bones in their new position.
Post-Surgical Orthodontics
After surgery, orthodontic treatment may continue for a few months to fine-tune the alignment of the teeth.
Recovery Process
Recovery from corrective jaw surgery is a gradual process that requires patience and adherence to the surgeon’s instructions.
Immediate Post-Surgery
- Swelling, bruising, and discomfort are common in the first few weeks.
- Pain management includes prescribed medications and cold compresses.
- A liquid or soft food diet is recommended to avoid straining the jaw.
Healing Phase
- The initial healing takes 6 to 8 weeks, but full recovery can take up to 12 months.
- Regular follow-ups with the surgeon and orthodontist are necessary.
- Gentle jaw exercises may be prescribed to restore mobility.
Long-Term Care
- Once fully healed, patients typically experience improved function and aesthetics.
- Maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups is essential.
Who Is a Candidate for Corrective Jaw Surgery?
Not everyone with jaw alignment issues requires surgery. An ideal candidate:
- Has significant jaw misalignment that cannot be corrected with orthodontics alone.
- Suffers from chronic pain, difficulty chewing, or breathing problems.
- Is physically healthy and has realistic expectations about the outcome.
- Has completed facial growth, typically around 18 years for females and 21 years for males.
Benefits of Corrective Jaw Surgery
Corrective jaw surgery offers a wide range of benefits that go beyond aesthetics:
Enhanced Functionality
Proper alignment improves chewing, biting, and speaking, leading to a better quality of life.
Aesthetic Improvements
Repositioning the jaw creates a more balanced facial appearance, boosting self-confidence.
Improved Oral Health
Correct alignment reduces the risk of tooth wear, gum disease, and TMJ disorders.
Better Breathing
For patients with sleep apnea or airway issues, surgery can result in easier, uninterrupted breathing.
Risks and Complications
Like any surgical procedure, corrective jaw surgery carries potential risks, including:
- Infection or bleeding.
- Nerve damage, causing temporary or permanent numbness.
- Relapse of the jaw to its previous position.
- Complications from anesthesia.
To minimize these risks, it’s crucial to choose a qualified and experienced surgeon and adhere to post-operative care instructions.
Cost of Corrective Jaw Surgery
The cost of corrective jaw surgery varies depending on factors such as the complexity of the case, the surgeon’s experience, and the geographic location. In general:
- The procedure may range from $20,000 to $50,000 or more.
- Health insurance may cover part of the cost if the surgery is deemed medically necessary.
Choosing the Right Surgeon
Selecting the right oral and maxillofacial surgeon is a critical step in achieving successful results. Consider the following:
- Credentials and Experience: Look for board-certified surgeons with extensive experience in corrective jaw surgery.
- Patient Reviews: Check testimonials and reviews to gauge patient satisfaction.
- Consultation: During your consultation, ask questions about the procedure, recovery, and potential risks.
Conclusion
Corrective jaw surgery is a highly effective solution for individuals with jaw misalignment or related issues. By improving both function and aesthetics, this procedure can significantly enhance one’s quality of life. While the process requires a considerable commitment, from pre-surgical orthodontics to recovery, the long-term benefits are well worth the effort.
If you’re considering corrective jaw surgery, consult with a qualified oral and maxillofacial surgeon to determine if it’s the right option for you. With proper planning and care, this life-changing procedure can deliver remarkable results.